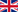
CANopenIA Coprocessor Mode
In coprocessor mode a CANopenIA is a coprocessor to another processor or microcontroller (the 'host'). The communication between the host and the CANopenIA can be implemented via a serial channel (typically UART, optionally I2C or SPI). The CANopen setup and configuration data including the Object Dictionary is stored in non-volatile memory such as an EEPROM or Flash memory. The configuration data is created with the CANopen Architect software package or dedicated setup utilities.
For most applications the bandwidth of the serial channel can be smaller than the bandwidth on the CANopen side as the communication between host and coprocessor is primarily an exchange of changing process data. The host can access the device's CANopen Object Dictionary using a simple command language. In summary, the communication on the serial channel includes:
- Events reported from the CANopenIA to the host
- Data arrived (data written into local dictionary)
- Also used to indicate changes in the network (nodes found / lost)
- Also used to indicate Network Management Master requests (reset, operation status change)
- Basic commands from host to CANopenIA
- Read data from a local Object Dictionary entry
- Write data to a local Object Dictionary entry (generates PDO, configuration dependant)
- Advanced commands from host to CANopenIA (only for Manager or CiA 447)
- Read data from an Object Dictionary entry of any node (by SDO client)
- Write data to an Object Dictionary entry of any node (by SDO client)
For more details about the communication protocol, see the CANopenIA remote access manual. ![]() (1.6 MB)
(1.6 MB)
The CANopen device and application profiles supported by the CANopenIA coprocessor mode include CiA 401 (generic I/O), CiA 404 (measuring devices and closed loop controllers), CiA 406 (encoders), CiA 410 (inclinometers), CiA 422 (CleANopen for municipal vehicles, selected virtual devices), CiA 443 (sub-sea SIIS level-2 devices), CiA 447 (car add-on, selected devices), CiA 454 (Energybus) and various others on request.